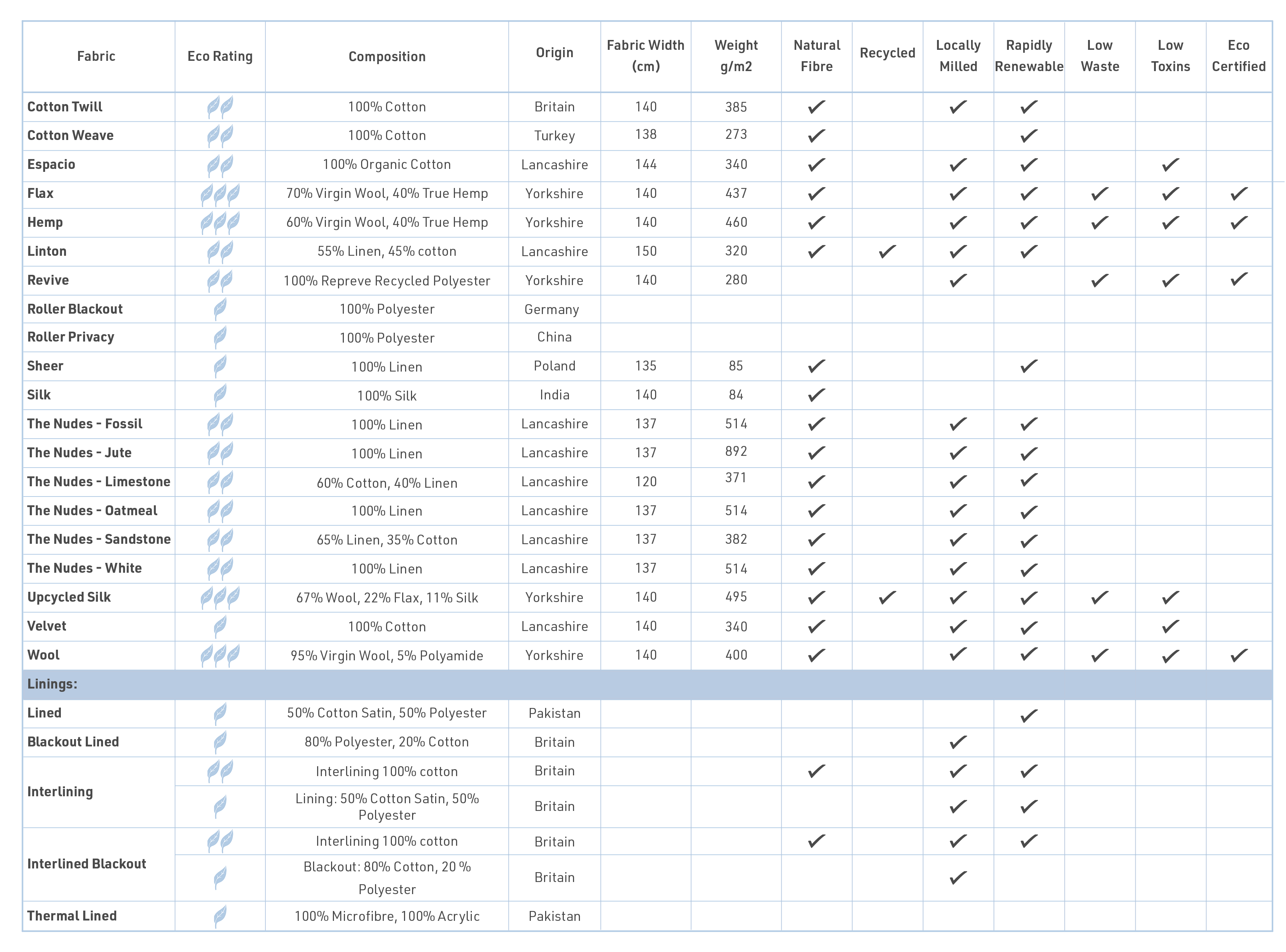
Fabric Comparison Chart
We want to be completely transparent about our fabrics and their eco credentials, so we have put together a simple comparison chart which includes our full fabric range including linings. Each eco criteria is outlined below.
Glossary
Natural Fibre - Natural fibre refers to the perfectly breathable fabric made of natural fibres that are extracted from plants or other bio sources. The main criteria in being referred to as a natural fibre are that the fabric must be biodegradable and should be derived from rapidly renewable environmentally sensitive sources. This feature rules out certain natural fabrics that undergo synthetic and non-eco-friendly extraction processes. Synthetic fibres on the other hand use significant energy and generate chemical waste in production.
Recycled - This fabric mainly aims to reduce the consumption of new materials and resources and hence is made from salvaged materials.
Locally Milled - Fabric is milled in our city and is directly shipped to the Curtains Dubai workshop. This reduces the overall carbon footprint and minimises fabric waste and above all helps support local industry.
Rapidly Renewable - This type of fabric is woven naturally from rapidly regenerating natural fibres without disturbing the ecology.
Low Waste - Minimal wastage of every resource including the raw materials, water and energy consumption during the production of fabric.
Low Toxins - There are no harmful chemicals exhaled during the fibre extrusion and dyeing process. And the finalised fabric product emits little VOCs.
What is a VOC? VOCs are organic chemicals that evaporate even under normal conditions thus intoxicating our interiors. These are actually the by-product of chemicals used in the manufacture of some household products, furnishings and paints. A high level of VOC is hazardous to health along with its contribution to global warming and climatic changes.
Eco Certified - Fabrics that have sustainable fabric certification from UAE Commission. Environmental performance is determined by considering the impact of fabric throughout its lifecycle.





















